-
Air Quality Forecast -
AQ Forecast by Site -
About
Community Air Monitoring
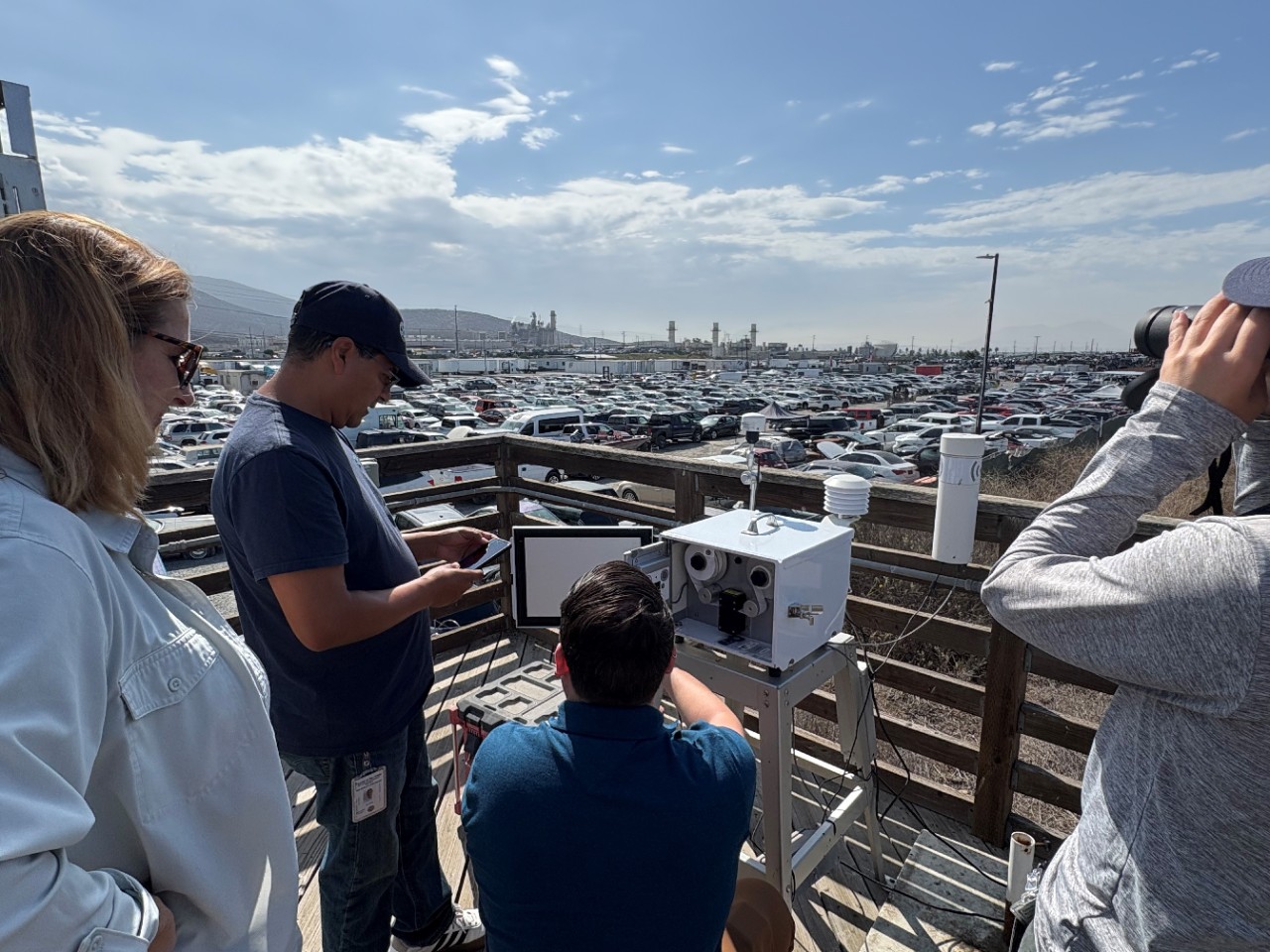
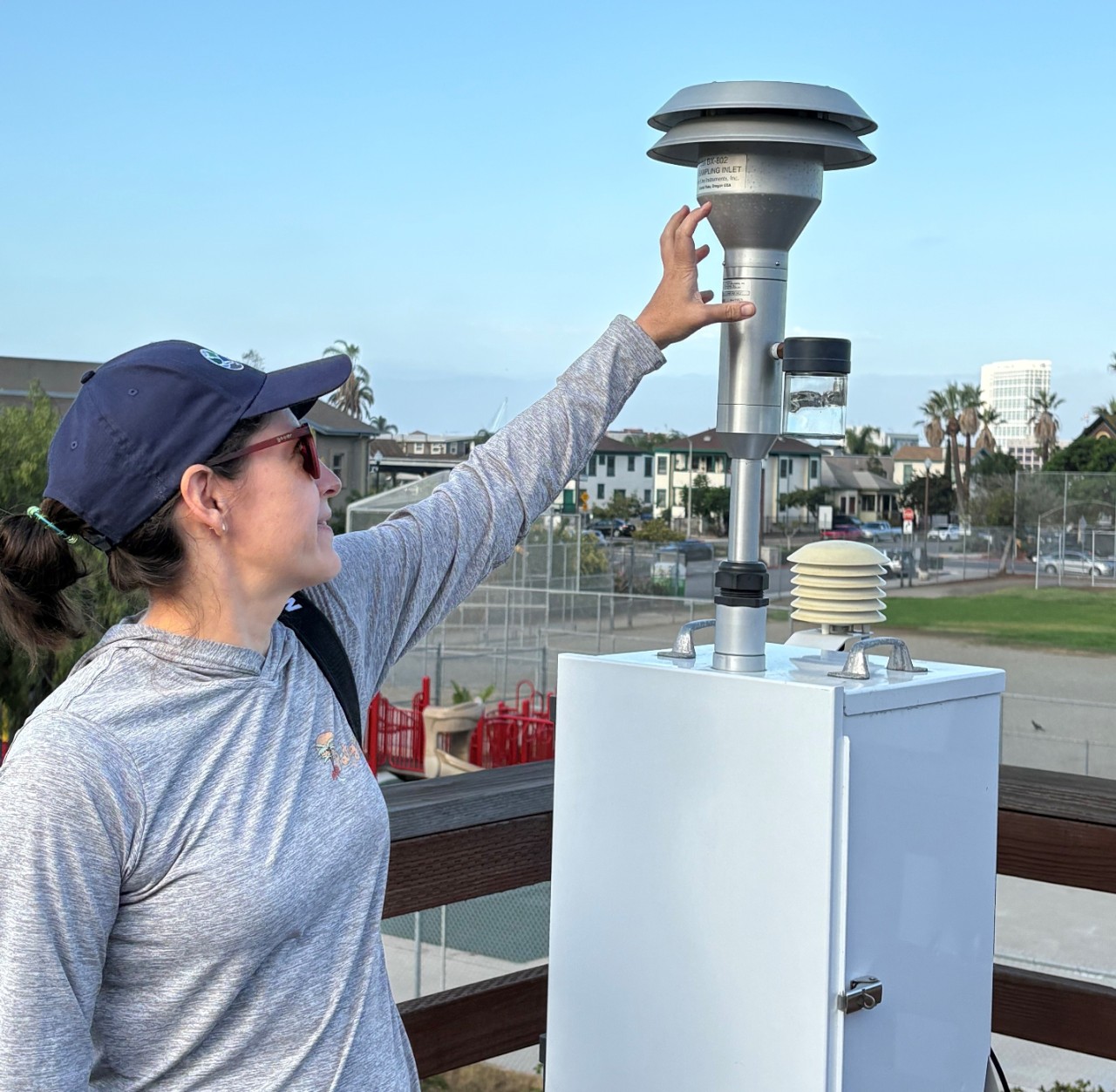
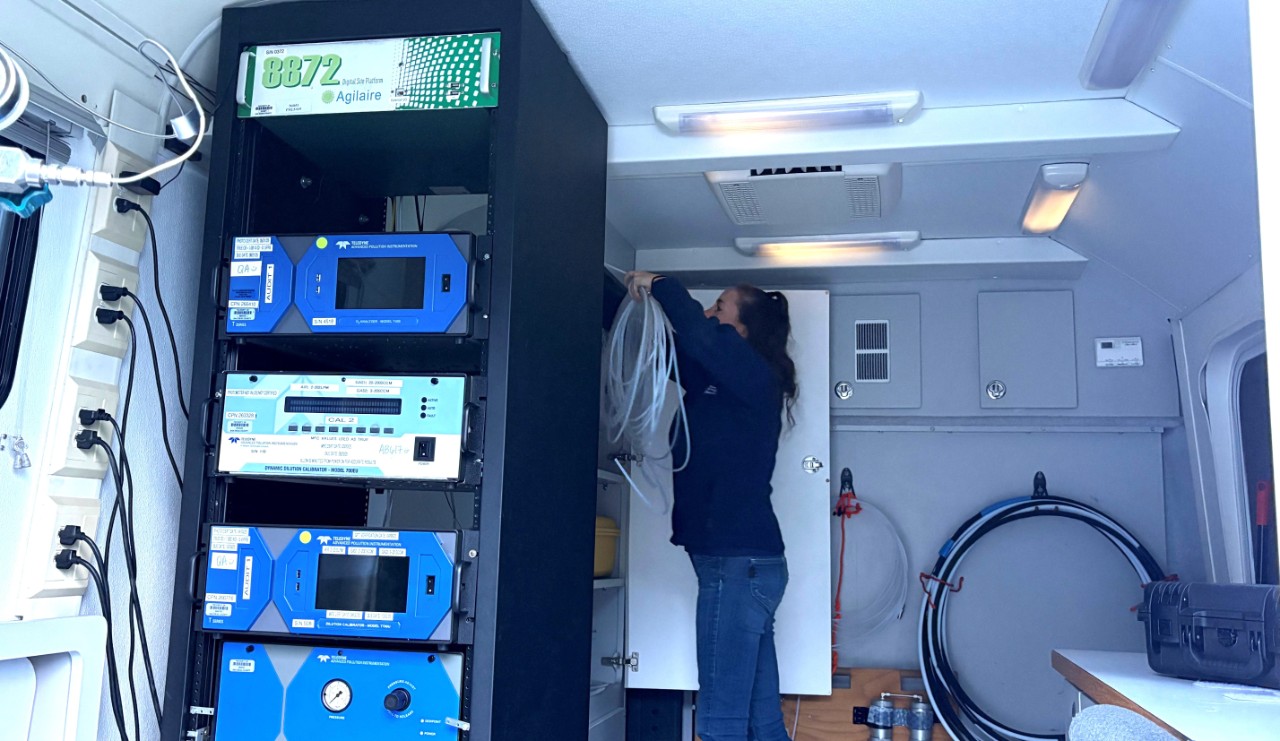
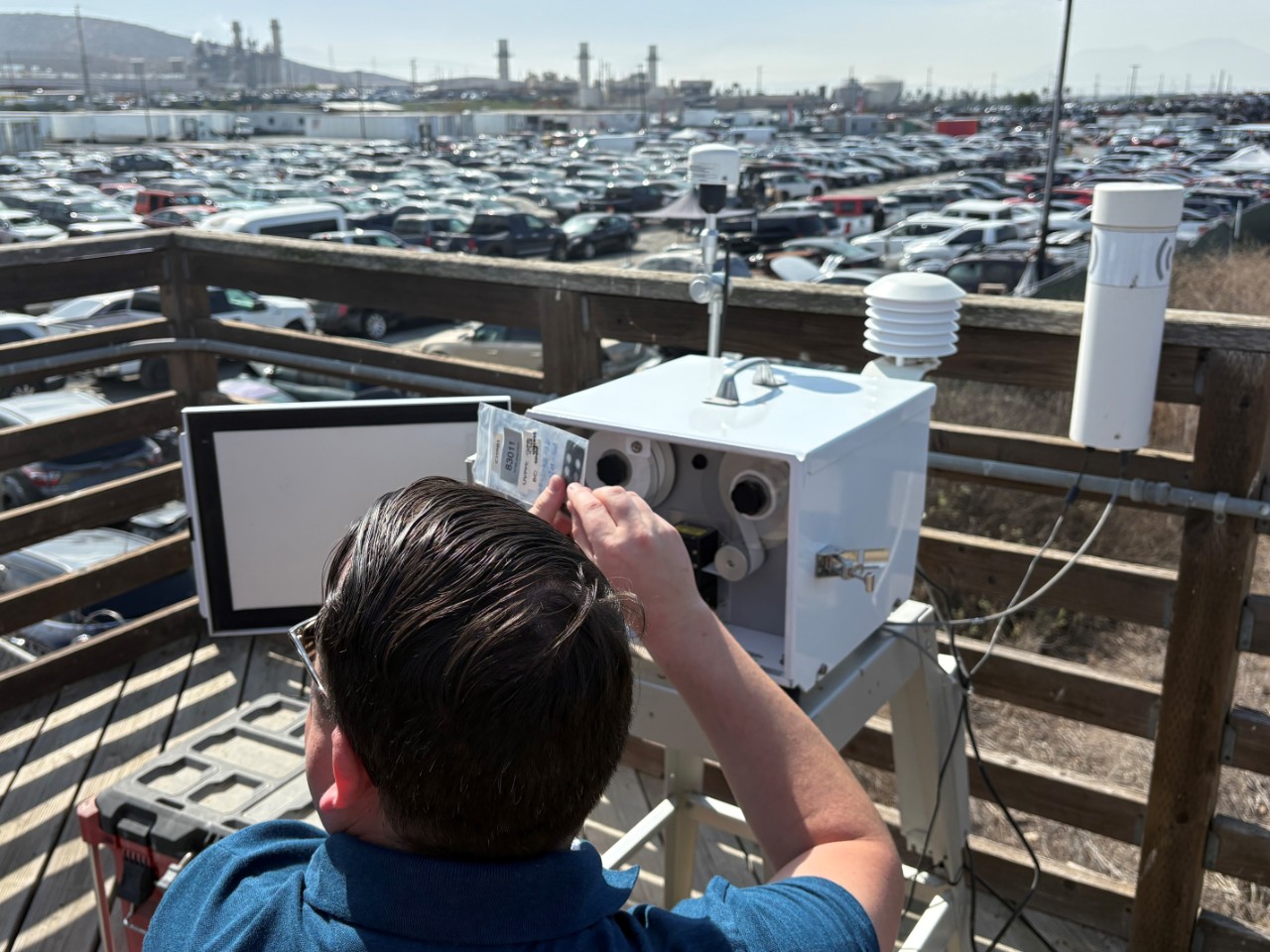
Air quality monitoring utilizes a network of sensors and specialized equipment to measure air pollution. It is important for understanding current air quality, as well as long-term trends in harmful emissions and exposure to air pollution.
Every day, the San Diego County Air Pollution Control District (SDAPCD) monitors air quality throughout the region to ensure compliance with air quality standards set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for criteria pollutants: Ozone, Particulate Matter, Carbon Monoxide, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide, and Lead. To learn more, visit the Regional Air Quality Monitoring page.
In addition, SDAPCD participates in the Community Air Protection Program (CAPP or AB 617), a statewide program focused on reducing pollution exposure in communities most impacted by air pollution. Through this program, SDAPCD’s Community Air Monitoring Team operates community-focused air quality monitors in two San Diego communities that experience higher pollution levels: the Portside Community near the Port of San Diego and the International Border Community near the U.S.–Mexico border.
In the Portside Communities the following air pollution is being monitored: airborne toxic metals, volatile organic compounds, and diesel particulate matter, measured through organic and elemental carbon (OCEC) in fine particulate matter (PM₂.₅) and black carbon. To learn more, visit the Portside Community Air Monitoring page.
In the International Border Communities the following air pollution is being monitored: hydrogen sulfide, airborne toxic metals, volatile organic compounds, Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, and Xylene (BTEX), and diesel particulate matter, measured through organic and elemental carbon (OCEC) in fine particulate matter (PM₂.₅) and black carbon. To learn more, visit the International Border Community Air Monitoring page.